What is periodontal disease / gum disease?
Periodontitis is common but largely preventable. It’s usually the result of poor oral hygiene. Brushing at least twice a day, flossing daily and getting regular dental checkups can greatly improve your chances of successful treatment for periodontitis and can also reduce your chance of developing it.
A general dentist or periodontist during regular examinations can easily detect periodontal disease. A periodontist is a dentist who specializes in the diagnosis, prevention and the treatment of gum disease.
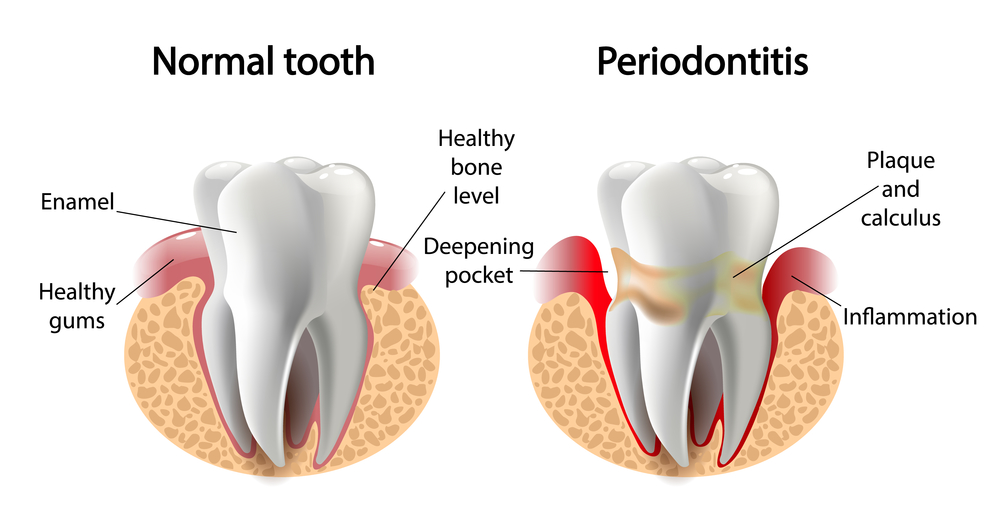
A periodontal charting will be performed for all teeth. An instrument called the periodontal probe, with ruled millimeter makings is used to measure the depth of the.space between the teeth and gums. Ideally, normal measurement ranges between 1 and 3mm. Depths greater than this may signify the presence of periodontal pockets and associated gum disease. X rays will also be taken to see the extent of bone damage that has occurred.
Signs and symptoms of periodontitis can include:
- Swollen or puffy gums
- Gums that feel tender when touched
- Gums that bleed easily
- New spaces developing between your teeth
Treatment may be performed by a periodontist, a dentist or a dental hygienist. The goal of periodontitis treatment is to thoroughly clean the pockets around teeth and prevent damage to surrounding bone. You have the best chance for successful treatment when you also adopt a daily routine of good oral care and stop tobacco use.
if periodontitis isn’t advanced, treatment may involve less invasive procedures, including:
- Scaling- Scaling removes tartar and bacteria from your tooth surfaces and beneath your gums. It may be performed using instruments, a laser or an ultrasonic device
- Root planing- Root planing smoothes the root surfaces, discouraging further buildup of tartar and bacteria, and removes bacterial byproducts that contribute to inflammation and delay healing or reattachment of the gum to the tooth surfaces
If you have advanced periodontitis, treatment may require dental surgery, such as:
- Flap surgery -Your periodontist makes tiny incisions in your gum so that a section of gum tissue can be lifted back, exposing the roots for more effective scaling and root planing. Because periodontitis often causes bone loss, the underlying bone may be recontoured before the gum tissue is sutured back in place. After you heal, it’s easier to clean these areas and maintain healthy gum tissue.
- Bone grafting-This procedure is performed when periodontitis has destroyed the bone surrounding your tooth root. The graft may be composed of small fragments of your own bone, or the bone may be synthetic or donated. The bone graft helps prevent tooth loss by holding your tooth in place. It also serves as a platform for the regrowth of natural bone.